CHEMICAL BONDING
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms or molecules that allows the formation of chemical compounds, which contain two or more atoms. A chemical bond is the attraction caused by the electromagnetic force between opposing charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of bonds varies considerably; there are "strong bonds" such as covalent or ionic bonds and "weak bonds" such as dipole-dipole interactions, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.
STRONG BOND
1- Ionic bonding
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that involves a metal and a nonmetal ion (or polyatomic ions such as ammonium) through electrostatic attraction. In short, it is a bond formed by the attraction between two oppositely charged ions.
2- Covalent bonding
A covalent bond is a form of chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms, and other covalent bonds. In short, the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding.[1]
WEAK BOND
1- Dipole-Dipole Forces
Are caused by permanent dipoles in molecules. When one atom is covalently bonded to another with a significantly different electronegativity, the electronegative atom draws the electrons in the bond nearer to itself, becoming slightly negative. Conversely, the other atom becomes slightly positive. Electrostatic forces are generated between the opposing charges and the molecules align themselves to increase the attraction (reducing potential energy).
2- The London dispersion force
The London dispersion force is the weakest intermolecular force. The London dispersion force is a temporary attractive force that results when the electrons in two adjacent atoms occupy positions that make the atoms form temporary dipoles. This force is sometimes called an induced dipole-induced dipole attraction. London forces are the attractive forces that cause nonpolar substances to condense to liquids and to freeze into solids when the temperature is lowered sufficiently.
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine (F,O, N). The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond. Usually the electronegative atom is oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, which has a partial negative charge. The hydrogen then has the partial positive charge. The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds.
UNIQUE FEATURES
A computer simulation, a computer model, or a computational model is a computer program, or network of computers, that attempts to simulate an abstract model of a particular system. Computer simulations have become a useful part of mathematical modeling of many natural systems in physics (computational physics), astrophysics, chemistry and biology, human systems in economics, psychology, social science, and engineering. Simulations can be used to explore and gain new insights into new technology, and to estimate the performance of systems too complex for analytical solutions.
Simulation provides a very useful help to us. Simulation helps teaching flows easily. With the moving or graphics that have been showed, it would helps students to understand easily . In this modern era, teachers should know how to use information and technology tools to help students learn and practice in a new way. So, they will have a new spirit and eager to get along with that particular subject. Sometimes simulation give an extra knowledge to us where we can understand more about the movement, the differences, pro and contra, and many more. So, we can get a better understand through simulation.
ENGAGE
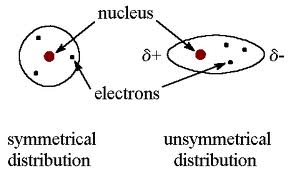
You are given the picture as shown below:
1. What is hydrogen bonding?
2. Explain more.
3. State the outcomes of hydrogen bonding.
EMPOWER
STEPS
- An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that involves a metal and a nonmetal ion through electrostatic attraction.
2. Sodium (2.8.1) has 1 electron more than a stable noble gas structure (2.8). If it gave away that electron it would become more stable.Chlorine (2.8.7) has 1 electron short of a stable noble gas structure (2.8.8). If it could gain an electron from somewhere it too would become more stable.The answer is obvious. If a sodium atom gives an electron to a chlorine atom, both become more stable.
3. Log on the web side and observe the animation to answer the question.
RESULT
QUESTIONS
1. What are the differences between ionic bonding and covalent bonding?
2. Explain briefly about the ionic bonding between sodium and chlorine.
3. List five features of ionic compounds.
ANSWERS
1.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- During the reaction of sodium with chlorine:
| sodium (on the left) loses its one valence electron to chlorine (on the right), |
| resulting in |
a positively charged sodium ion(left) and a negatively charged chlorine ion (right). |
3. Ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals.
- In naming simple ionic compounds, the metal is always first, the nonmetal second (e.g., sodium chloride).
- In solution, ionic compounds easily conduct electricity.
- Ionic compounds tend to form crystalline solids with high melting temperatures.
ENHANCE
| A simple way of assigning descriptive labels to bonds is to assume that metal-nonmetal and metal-polyatomic bonds are ionic and that nonmetal-nonmetal bonds, with two qualifications are polar covalent. Bonds between two atoms of the same element and the carbon-hydrogen bond should be considered nonpolar covalent. Electonegativity differences can also be used but for the purposes of this exercise, use the above guidelines to classify the bonds in each formula unit.
| |||
| | ionic | ||
| | polar covalent | ||
| | Non polar covalent | ||
| | None of the previous answers. | ||
| | |||
| 2. | NO | ||
| | ionic | ||
| | polar covalent | ||
| | Non polar covalent | ||
| | None of the previous answers. | ||
| | |||
| 3. | HCl | ||
| | ionic | ||
| | polar covalent | ||
| | nonpolar covalent | ||
| | None of the previous answers. | ||
| | |||
| 4. | MgO | ||
| | ionic | ||
| | polar covalent | ||
| | Non polar covalent | ||
| | None of the previous answers. | ||
| | |||
| 5. | CH4 | ||
| | ionic | ||
| | polar covalent | ||
| | Non polar covalent | ||
| | None of the previous answers. | ||
| | |||
| 6. | KF | ||
| | ionic | ||
| | polar covalent | ||
| | nonpolar covalent | ||
| | None of the previous answers. | ||
| | |||
| 7. | CCl4 | ||
| | ionic | ||
| | polar covalent | ||
| | Non polar covalent | ||
| | None of the previous answers. | ||
| | |||
| 8. | NH3 | ||
| | ionic | ||
| | polar covalent | ||
| | Non polar covalent | ||
| | None of the previous answers. | ||










No comments:
Post a Comment